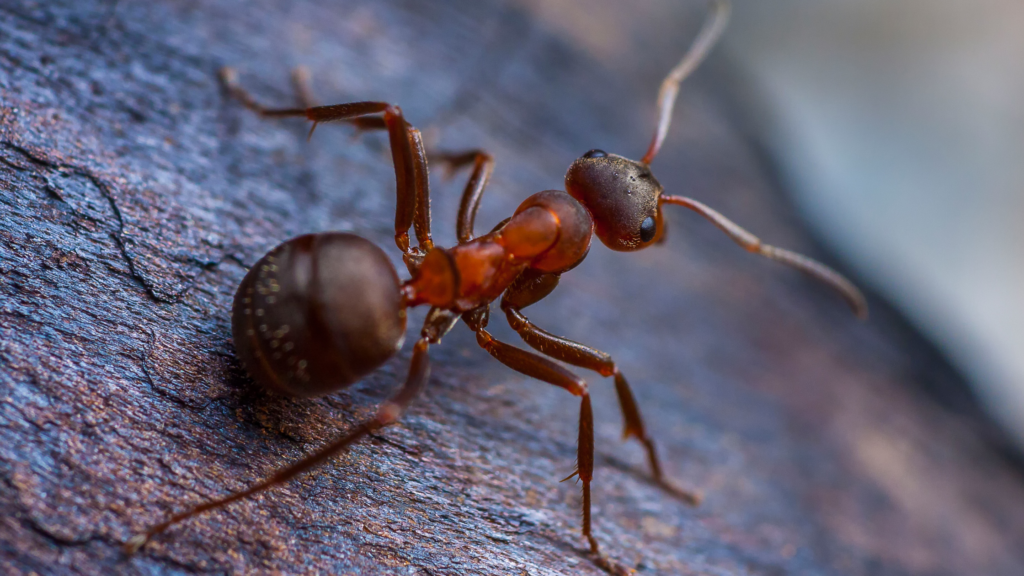
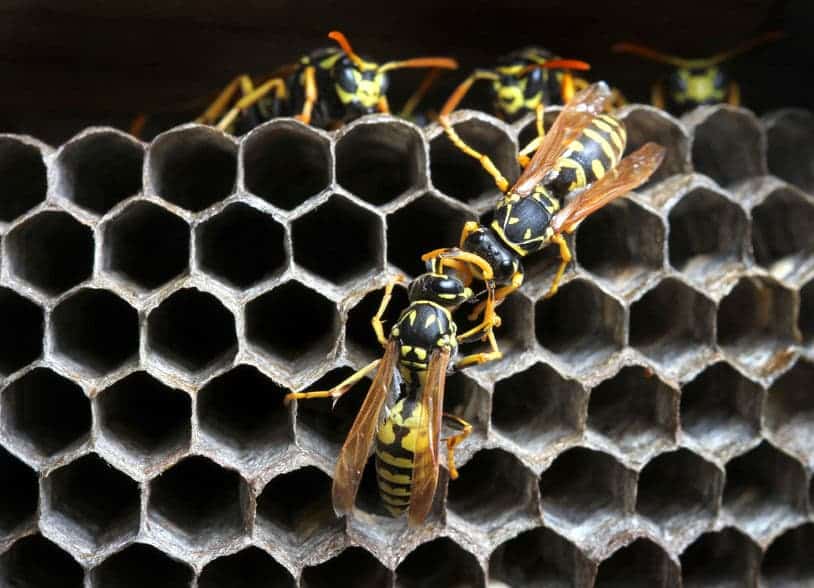
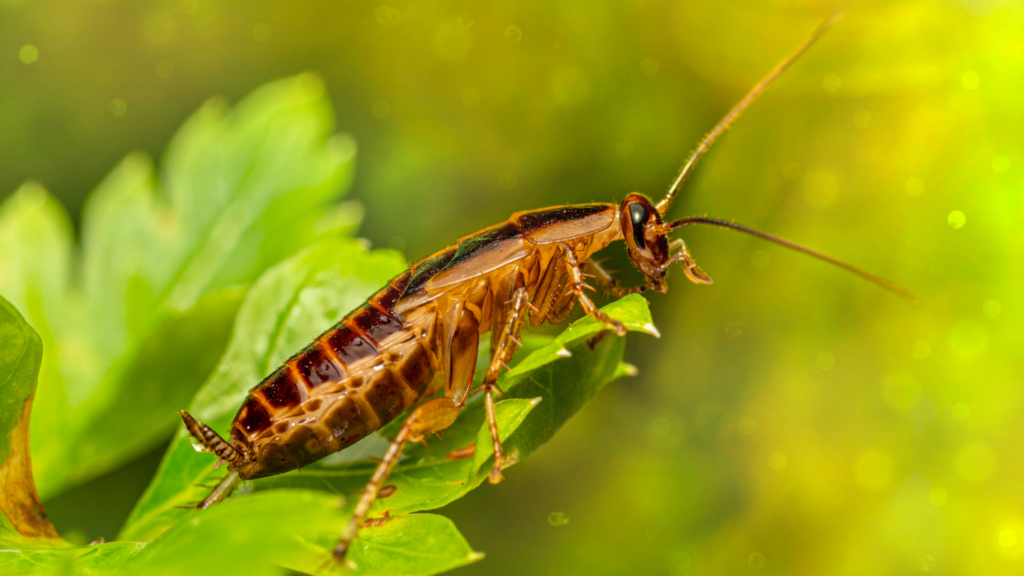
Identify common pests with help from our pest library guide. From mosquitoes to bats to earwigs, call Turner Pest Control if they appear in or around your home!
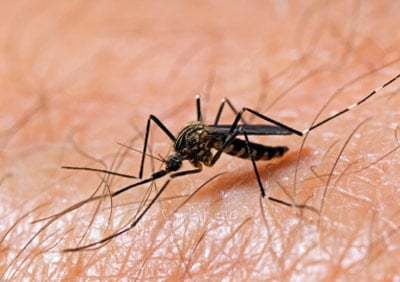
Mosquito
HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Prefers wooded and watery areas
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Typically, both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar and plant juices, but in many species the mouthparts of the females are adapted for piercing the skin of animal hosts and sucking their blood as ectoparasites. Both plant materials and blood are useful sources of energy in the form of sugars, and blood also supplies more concentrated nutrients, such as lipids, but the most important function of blood meals is to obtain proteins as materials for egg production.
DISTRIBUTION
Throughout the United States and the world
Black Widow

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Settles in higher places with a silky web and in dry, protected areas after web is left, barns, outhouses, sheds, etc.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Spins a silky web to capture prey. Bites with a neurotoxin venom. Female is usually shy but becomes aggressive after egg laying and while guarding the eggs.
DISTRIBUTION
Throughout the United States and the world
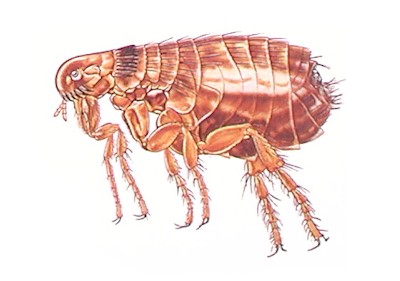
Cat Flea
HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Found typically where animals sleep or frequent because larvae live in areas of high moisture.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Known for their discomforting bites and for transmitting the plague and other infectious diseases. May be a problem for those with or without pets do to their jumping abilities. Usually finds host to attach to and live off of.
DISTRIBUTION
Throughout the United States and the world
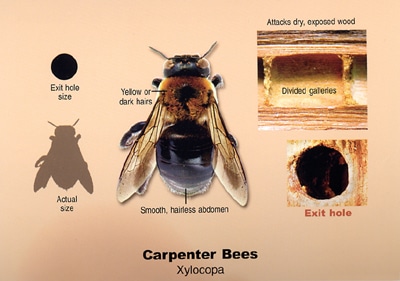
Carpenter Bee
HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Females prefer to excavate nest tunnels in exposed, unfinished wood, but are not limited to it.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Adults overwinter in old nest tunnels and excavate new tunnels in the spring. Development from egg to adult takes roughly five weeks. Males do not have a stinger, although females do, but is rarely used.
DISTRIBUTION
Found in the eastern United States
Scorpion

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Scorpions prefer to live in areas where the temperatures range from 20 to 37 °C (68 to 99 °F), but may survive freezing temperatures to the desert heat. They are nocturnal and fossorial, finding shelter during the day in the relative cool of underground holes or undersides of rocks and coming out at night to hunt and feed.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
They usually hid in or behind something in the day to conserve water. Scorpions mostly feed on insects. A scorpion’s sting contains a neurotoxin venom that may result in death from allergies or respiratory paralysis. Though the scorpion has a fearsome reputation as venomous, only about 25 out of 1,752 species are known to have venom capable of killing a human being.
DISTRIBUTION
South and southwest United States
Silverfish

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
All silverfish species hide during the day and prefer to hide or rest in right cracks or crevices. They can be found almost anywhere in a house including living rooms, bedrooms, bathroom, attics, basements and garages. Silverfish can also infest commercial structures such as offices, stores, and libraries. They tend to roam quite some distance while searching for food, but once they find a satisfactory food source, they remain close to it.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Silverfish can survive for weeks without food or water. They prefer areas of room temperature and high relative humidity. They prefer proteins to carbohydrates and are cannibalistic. Silverfish are often introduced into building via cardboard cartons of books and papers from an infested location. They are pest of paper, particularly of glazed paper and paper with wallpaper paste, etc. Silverfish eat proteins such as dried beef and dead or injured of their kind.
DISTRIBUTION
Found throughout the U.S. and the world
Earwig

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Stays outside in protected situations in winter otherwise it buries itself in the ground. Nocturnal insects that feed on dead plants and/or insects.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Known for distinct odor that is released when they are crushed. Occasionally kills vegetables, flowers, fruits, and trees.
DISTRIBUTION
Throughout the United States and the world
Stink Bug

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
For Green Stink Bugs, host plants include mainly orange trees, cherry trees, soybean, and apple trees. They cause significant damage to gardens and farms for they mostly remain unnoticed by the farmers on account of their green color. Furthermore, they use green plant not only as a food but also as a safe haven during their breeding period. Here they lay eggs on host plants in an excessive number and increase their race.
For Brown Stink Bugs, their major hosts include maple, birch, serviceberry, catalpa, butterfly bush, pecan, redbud, hackberry, pepper, dogwood, citrus, cucumber, tomato, sunflower, apple, pear, plum, and grape. Brown stink bugs use their proboscis to suck the host plants and resultantly they not only create necrotic areas on the surface of fruits but also even cause seed loss and transfer of plant pathogens.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
The name stink bug derives from their tendency to eject a foul smelling glandular substance secreted from pores in the thorax when disturbed; in some species, the liquid contains cyanide compounds with a rancid almond scent. This is a form of antipredator adaptation.
DISTRIBUTION
Southern United States
Gnat

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Gnats thrive outside when conditions are both moist and warm. However, due to their small size and ability to both reproduce quickly and in many situations, gnats can easily be found thriving inside mostly any structure.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
The adult stage is the one, which people find to be so annoying and persistent. Eye gnats will regularly land on or around one’s eye and nose; black flies or buffalo gnats will land anywhere they can find skin on which to suck blood. Essentially that is all the females want; blood. They will seek this from any mammal they can find and people will often times be their prime target.
DISTRIBUTION
Prevalent throughout most of the world
Bat

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Thirteen species of bats live in Florida year-round. All twilight and free-tailed bats from eastern North America are insect eaters and can be divided into two groups: those that spend a portion of the year in caves and those that roost in other structures. When caves and trees are scarce, bats may roost in man-made structures such as buildings, bridges, culverts, and bat houses.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Although most bats are insect eaters, some bats specialize in eating other items such as fruit, nectar and pollen, vertebrates, and even blood. All bats resident in Florida eat insects, but a few of the species that occasionally show up in south Florida feed on fruit, nectar, and pollen.
DISTRIBUTION
Worldwide distribution
Rice Weevil

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Since the larvae are subterranean, they are rarely seen. Adults are typically nocturnal and remain concealed on the plant or in the litter or soil during the daytime. All weevils will enter structures when conditions outdoors become adverse.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
They mostly spend the winter as almost-mature larvae in the soil among the host plant’s roots. They pupate in the spring near the soil surface. Adults emerge from early May to late July.
DISTRIBUTION
Found throughout most of the U.S. and Canada
Pest Control Library | Ants | Beetles | Cockroaches | Termites | Other Pests



