Don’t let these biting insects keep bothering you. Let us help.
We’ll identify the biting bugs you have and provide the best solution.
PEST CONTROL LIBRARY
Biting Insects

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Prefers wooded and watery areas
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Typically, both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar and plant juices, but in many species the mouthparts of the females are adapted for piercing the skin of animal hosts and sucking their blood as ectoparasites. Both plant materials and blood are useful sources of energy in the form of sugars, and blood also supplies more concentrated nutrients, such as lipids, but the most important function of blood meals is to obtain proteins as materials for egg production.
DISTRIBUTION
Throughout the United States and the world
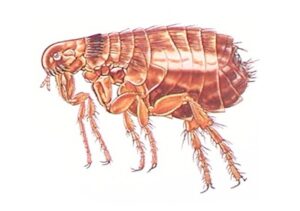
HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Found typically where animals sleep or frequent because larvae live in areas of high moisture.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
Known for their discomforting bites and for transmitting the plague and other infectious diseases. May be a problem for those with or without pets do to their jumping abilities. Usually finds host to attach to and live off of.
DISTRIBUTION
Throughout the United States and the world

HABITAT/WOOD PREFERENCE
Gnats thrive outside when conditions are both moist and warm. However, due to their small size and ability to both reproduce quickly and in many situations, gnats can easily be found thriving inside mostly any structure.
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
The adult stage is the one, which people find to be so annoying and persistent. Eye gnats will regularly land on or around one’s eye and nose; black flies or buffalo gnats will land anywhere they can find skin on which to suck blood. Essentially that is all the females want; blood. They will seek this from any mammal they can find and people will often times be their prime target.
DISTRIBUTION
Prevalent throughout most of the world
Although these flies—sometimes called “sheep flies”—may not look intimidating, they can be nasty creatures because of their bloodsucking behaviors. These yellow-hued flies are a bit bigger than the ubiquitous eight-to-quarter-inch house fly although their eyes are a different color: bright green or gold. Their size ranges from ¾ – 1-¼ inch. Their wings are large and clear, with dark bands in them. Females are most active during the day.
Males of the species spend their time seeking pollen while the females, unfortunately, feed on blood. We’re using the word “feed” rather than “bite” because the female deer fly uses its jaw and sharp parts in its mouth to slice the skin. As the host (victim!) bleeds, the fly uses its sponge-like mouth to soak up the fluid.
Its saliva contains an anticoagulant because this pest wants to feed on as much blood as possible per slice, which means that a person may bleed a bit afterwards. The spots can itch and be mildly painful; these symptoms can go up in intensity as the number of bites increase. If you’ve got a fly infestation that includes this species, contact us for deer flies’ pest control services.

